工具调用 Tool Calling
作用
工具调用允许模型与 API 或工具进行交互,从而增强其功能。
工具主要用于两个场景:
获取信息:从外部来源(例如数据库、Web 服务、文件系统或 Web 搜索引擎)获取信息。其目标是增强模型的知识,使其能够回答原本无法回答的问题。因此,它们可用于检索增强生成 (RAG)场景。例如,可以使用工具检索给定位置的当前天气、检索最新新闻文章或查询数据库中的特定记录采取行动:用于在系统中采取行动,例如发送电子邮件、在数据库中创建新记录、提交表单或触发工作流。其目标是自动化原本需要人工干预或明确编程的任务。例如,预订航班、在网页上填写表单,或在代码生成场景中基于自动化测试 (TDD) 实现 Java 类
需要注意的是:不是所有的模型都支持工具调用,请选择能够处理工具调用的模型,例如:qwen3:30b-a3b-instruct-2507-q4_K_M
核心原理
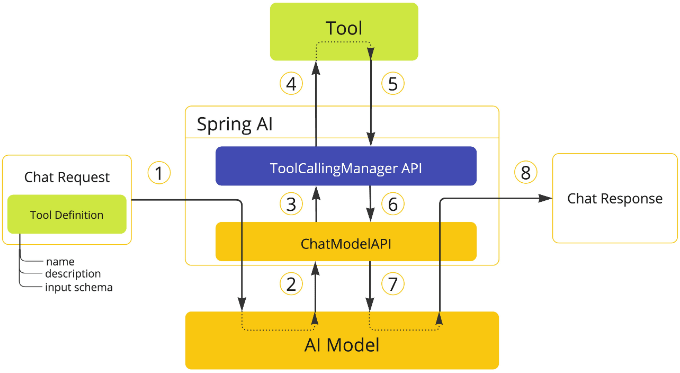
说明:
- 客户端发送请求,包含
prompt和可用工具列表,通过ChatModel发送给模型进行模型调用 - 当模型需要调用某个工具时,它会返回响应(
ChatResponse),其中包含工具名称和根据 inputSchema 定义的请求参数 ChatModel将工具调用请求发送到ToolCallingManager(ToolCallingManager用于处理整个工具的执行周期)ToolCallingManager识别要调用的工具并使用提供的输入参数执行它- 工具调用的结果返回给
ToolCallingManager ToolCallingManager将工具执行结果返回给ChatModel- 如果工具的
returnDirect属性为true,ChatModel直接将工具结果返回给调用者(ChatClient),流程结束;否则,ChatModel将工具执行结果发送回给模型(ToolResponseMessage) 后,继续执行第 8 步 - 模型使用工具调用结果作为附加上下文生成最终响应,并通过
ChatResponse将其发送回调用者(ChatClient)
核心接口
两个核心接口:工具 ToolCallback 与工具执行管理器 ToolCallingManager。工具负责定义工具(包括工具定义和工具执行逻辑);工具执行管理器负责管理工具的执行,其直接与 ChatModel 沟通,是工具执行的门面接口。
工具
java
public interface ToolCallback {
/**
* Definition used by the AI model to determine when and how to call the tool.
* 工具核心定义:name/description/inputSchema
*/
ToolDefinition getToolDefinition();
/**
* Metadata providing additional information on how to handle the tool.
* 定义:returnDirect
*/
ToolMetadata getToolMetadata();
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and return the result to send back to the AI
* model.
* 执行逻辑
*/
String call(String toolInput);
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and context, and return the result to send back
* to the AI model.
* 带着上下文执行逻辑
*/
String call(String toolInput, @Nullable ToolContext toolContext);
}java
public interface ToolDefinition {
/**
* The tool name. Unique within the tool set provided to a model.
*/
String name();
/**
* The tool description, used by the AI model to determine what the tool does.
*/
String description();
/**
* The schema of the parameters used to call the tool.
*/
String inputSchema();
}SpringAI 默认为 ToolCallback 接口提供了两个实现:MethodToolCallback 和 FunctionToolCallback<I, O>,前者用于实现方法工具,后者用于实现函数工具。
工具管理器
java
public interface ToolCallingManager {
/**
* Execute the tool calls requested by the model.
* 执行工具
*/
ToolExecutionResult executeToolCalls(Prompt prompt, ChatResponse chatResponse);
}框架判断是否要执行工具的逻辑如下:
java
public class DefaultToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate implements ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate {
@Override
public boolean test(ChatOptions promptOptions, ChatResponse chatResponse) {
// 开启内部控制标识 && 模型返回了需要执行的工具
return ToolCallingChatOptions.isInternalToolExecutionEnabled(promptOptions) && chatResponse != null
&& chatResponse.hasToolCalls();
}
}方法工具定义与调用
定义工具执行管理器
java
@Bean
public ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager() {
return ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
}
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient2(ChatModel chatModel) {
return ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
}定义工具
java
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.model.ToolContext;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
/**
* 天气工具类
*/
public class WeatherTools {
@Tool(name = "getWeather", description = "getWeather", returnDirect = false)
public Weather getWeather(@ToolParam(description = "The location of the weather") Location location) {
if (location == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Location cannot be null");
}
if (location.hangzhou()) {
return new Weather()
.setCurrentLocation(location)
.setCurrentWeather(new Weather.WeatherInfo()
.setTemperature(40.0)
.setWeatherDescription("晴"));
} else {
return new Weather()
.setCurrentLocation(location)
.setCurrentWeather(new Weather.WeatherInfo()
.setTemperature(30.3)
.setWeatherDescription("阴"));
}
}
@Tool(name = "setAlarm", description = "if the given temperature exceeds 37 degrees, please set a warning", returnDirect = true)
public void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "weather, contains currentLocation and currentWeather") Weather weather, @ToolParam(description = "The tool context", required = false) ToolContext toolContext) {
System.out.println("Warning: The temperature in " + weather.getCurrentLocation().getCity() + " is " + weather.getCurrentWeather().getTemperature() + "°C. 注意避暑,以下时避暑指南:" + toolContext.getContext().get("summerHeatEscapeGuide"));
}
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class Location {
@ToolParam(description = "The province of the location")
private String province;
@ToolParam(description = "The city of the location")
private String city;
@ToolParam(description = "The area of the location", required = false)
private String area;
public boolean hangzhou() {
return "Hangzhou".equals(city);
}
}
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class Weather {
private Location currentLocation;
private WeatherInfo currentWeather;
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class WeatherInfo {
private Double temperature;
private String weatherDescription;
}
}
}说明:
@Tool将一个方法标识为一个工具name:工具名称,如果不填,默认使用方法名。是工具的唯一标识,建议自行填写,并且全局唯一description:工具用途。务必详尽的介绍该工具的功能,模型会根据该描述进行工具的选择returnDirect:false-表示工具的返回需要返回给模型,模型会根据该返回结果做推理逻辑,将最终的结果返回给客户端;true-表示工具的返回直接返回给客户端,不需要返回给模型resultConverter:用于将工具返回的结果序列化为 String 返回给模型
@ToolParam:标识工具参数的作用,可用于方法参数和属性上。描述务必详细一些,例如setAlarm中的@ToolParam(description = "weather, contains currentLocation and currentWeather") Weather weather,如果仅描述为the weather information,将无法正确的接收来自getWeather()的结果ToolContext:工具上下文参数,可以从ChatClient传入- 支持的方法范围:静态方法和实例方法;public/protected/default/private 可见性;包含该方法的类可以是顶级类或嵌套类,也可以具有任意可见性
- 支持的方法参数范围:方法可以定义任意数量的参数(包括无参数),并且支持大多数类型(primitives, POJOs, enums, lists, arrays, maps)
- 支持的方法返回值范围:方法可以返回大多数类型,包括 void。如果该方法返回值,则返回类型必须是可序列化类型,因为结果将被序列化并发送回模型
- 方法工具不支持的参数类型和返回值类型:
Optional/Asynchronous types (e.g. CompletableFuture, Future)/Reactive types (e.g. Flow, Mono, Flux)/Functional types (e.g. Function, Supplier, Consumer),其中函数类型可以由函数工具支持
执行工具
java
@RequestMapping("/3")
public String execute3() {
return chatClient2.prompt("What is the weather like in Hangzhou?")
.tools(new WeatherTools()) // 添加工具
.call().content();
}
@RequestMapping("/4")
public String execute4() {
return chatClient2.prompt("If the temperature in Hangzhou is above 37 degrees, please set a warning.")
.tools(new WeatherTools()) // 添加工具
.toolContext(Map.of("summerHeatEscapeGuide", "多喝水"))
.call().content();
}根据消息流转看下执行步骤:
text
1.USER: If the temperature in Hangzhou is above 37 degrees, please set a warning. // 发送用户消息给模型
2.ASSISTANT: ToolCall[function=ToolCallFunction[name=getWeather, arguments={location={city=Hangzhou}}, index=null]] // 模型返回需要调用的工具
3.TOOL: {"currentLocation":{"province":null,"city":"Hangzhou","area":null},"currentWeather":{"temperature":40.0,"weatherDescription":"晴"}} // 工具返回的响应
4.将前三个消息一起发送给模型
5.ASSISTANT: ToolCall[function=ToolCallFunction[name=setAlarm, arguments={weather={currentLocation={area=null, city=Hangzhou, province=null}, currentWeather={temperature=40, weatherDescription=晴}}}, index=null]] // // 模型返回需要调用的工具
6.TOOL:null // 工具返回给客户端底层原理
WeatherTools 的两个方法 getWeather 和 setAlarm 在底层运行时会转换为两个 MethodToolCallback,其中 getWeather 的信息如下。核心注意下 inputSchema,通过 jsonSchema 定义清楚了入参,如果后续需要手动定义 inputSchema,这个可以作为参考示例。
text
MethodToolCallback{toolDefinition=DefaultToolDefinition[name=getWeather, description=getWeather, inputSchema={
"$schema" : "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema",
"type" : "object",
"properties" : {
"location" : {
"type" : "object",
"properties" : {
"area" : {
"type" : "string",
"description" : "The area of the location"
},
"city" : {
"type" : "string",
"description" : "The city of the location"
},
"province" : {
"type" : "string",
"description" : "The province of the location"
}
},
"required" : [ "city", "province" ],
"description" : "The location of the weather"
}
},
"required" : [ "location" ],
"additionalProperties" : false
}], toolMetadata=DefaultToolMetadata[returnDirect=false]}函数工具定义与调用
定义工具
java
public class GetWeatherTool implements Function<GetWeatherTool.Location, GetWeatherTool.Weather> {
@Override
public Weather apply(@ToolParam(description = "The location of the weather") Location location) {
if (location == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Location cannot be null");
}
if (location.hangzhou()) {
return new GetWeatherTool.Weather()
.setCurrentLocation(location)
.setCurrentWeather(new Weather.WeatherInfo()
.setTemperature(40.0)
.setWeatherDescription("晴"));
} else {
return new GetWeatherTool.Weather()
.setCurrentLocation(location)
.setCurrentWeather(new Weather.WeatherInfo()
.setTemperature(30.3)
.setWeatherDescription("阴"));
}
}
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class Location {
@ToolParam(description = "The province of the location")
private String province;
@ToolParam(description = "The city of the location")
private String city;
@ToolParam(description = "The area of the location", required = false)
private String area;
public boolean hangzhou() {
return "Hangzhou".equals(city);
}
}
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class Weather {
private Location currentLocation;
private WeatherInfo currentWeather;
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class WeatherInfo {
private Double temperature;
private String weatherDescription;
}
}
}说明:
@ToolParam:标识工具参数的作用,可用于方法参数和属性上- 支持的函数参数和返回范围:函数入参和返回必须是
public的 - 函数工具不支持的参数返回值范围:
Primitive types/Optional/Collection types (e.g. List, Map, Array, Set)/Asynchronous types (e.g. CompletableFuture, Future)/Reactive types (e.g. Flow, Mono, Flux).
执行工具
java
@RequestMapping("/5")
public String execute5() {
FunctionToolCallback<GetWeatherTool.Location, GetWeatherTool.Weather> getWeather = FunctionToolCallback
.builder("getWeather", new GetWeatherTool()) // name 和实例
.description("getWeather") // 描述
.inputType(GetWeatherTool.Location.class) // 输入参数类型,如果未主动指定 inputSchema,则使用这个参数类型生成 inputSchema = JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForType(this.inputType)
.toolMetadata(ToolMetadata.builder().returnDirect(false).build())
.build();
return chatClient2.prompt("What is the weather like in Hangzhou?")
.toolCallbacks(List.of(getWeather)) // 添加工具
.call().content();
}文章的最后,如果您觉得本文对您有用,请打赏一杯咖啡!感谢!
